Simulating Serial Devices: Shorten Development Cycles Time and Hardware Expenditure

If you’re developing a new software or hardware product based on serial communication, like a barcode reader, GPS unit, or specialty sensor, there is most likely one big roadblock: you often don’t have the actual device available or ready for testing. That’s when simulating serial devices saves the day.
In this article, we’ll explore what it means to simulate a serial device, why it’s useful, and how it can save both time and money during development. If you want to test, then you can use free serial port communication software to understand how it can help you in saving your time.
What Is Serial Device Simulation?
Serial device simulation is the procedure of creating a virtual image of a real physical device communicating over a serial port. Instead of waiting for the real hardware, you can simulate how the device would exchange and receive information using software tools like Advanced Serial Port Monitor.
This way, you can test your application or system as if the device was there—whether it is or not.
Why Simulate a Serial Device?
If you’re writing a software application that reads from a temperature sensor. But the sensor is delayed in shipping, or too expensive to buy multiple to test with.
Don’t stall development or make an educated guess. You can simulate that sensor. You can create a virtual serial port and have it send sample temperature values every few seconds—just like the real sensor would.
That is:
- You don’t need the actual hardware
- You can test your software early
- You can simulate different scenarios, like errors or unexpected data
Imagine you’re part of a team building a POS (Point of Sale) system for a retail store. The system needs to read barcodes, process transactions, and print receipts. You’re still waiting for the barcode scanner to arrive, but your deadline is tight.
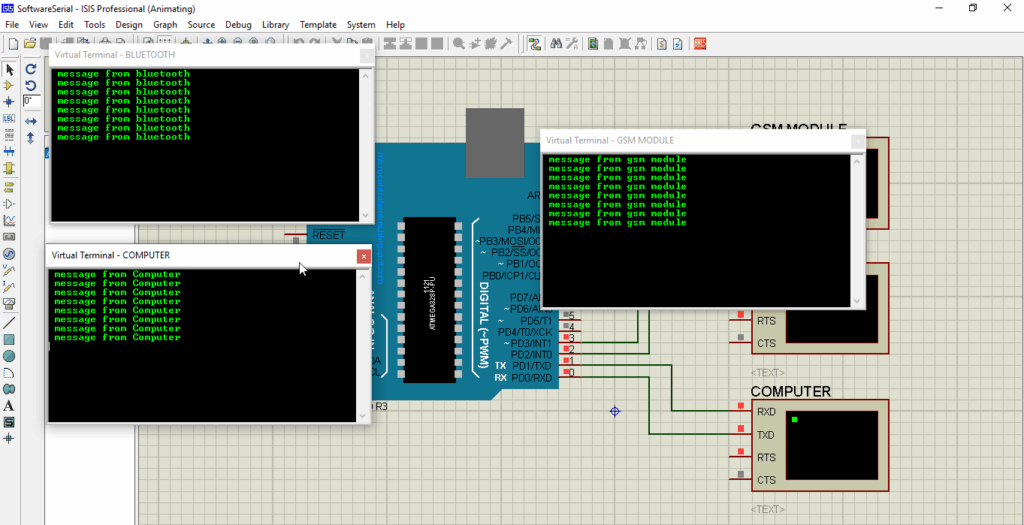
Rather than just sitting around, your programmer mimics the barcode scanner by way of a serial port monitor software. You press a button, and the software inputs dummy barcode information into your system. You can then test out different reactions your software responds with, whether it scans the data correctly and how it stores it.
By the time the real scanner does arrive, your software is 90% complete—and tested.
Save Time in Development
One of the biggest benefits of simulation is time saving. In traditional workflows, developers sit idle waiting for the hardware to be available in order to test. With simulation, however, you can code and test in parallel—software teams do not need to wait for the hardware team to finish first.
You can even verify thousands of corner cases that are hard to reproduce with real hardware—e.g., data corruption, comms failures, or random drops.
Save on Hardware
Hardware is expensive, especially when you need to test with multiple devices. Serial device emulation enables you to test on many systems without having to spend 10 GPS modules or bar-code scanners.
This is great for small startups, hobbyists, or small groups who want to maintain costs as low as possible but still make excellent solutions.
Serial device simulation is like having a “digital twin” of your hardware. It speeds up development, enables you to catch bugs early, and saves you money on hardware costs. Whether you’re creating industrial systems, embedded applications, or just trying out a side project, this approach can make your work easier and more efficient.


 Unlocking the Truth: What TruthFinder Can and Cannot Reveal About People
Unlocking the Truth: What TruthFinder Can and Cannot Reveal About People  Free online grade books – A teacher’s best friend in modern education
Free online grade books – A teacher’s best friend in modern education  Gold Market Chronicles: Tales of Rates and Investments
Gold Market Chronicles: Tales of Rates and Investments  Upholding Web Excellence with Professional WordPress Maintenance
Upholding Web Excellence with Professional WordPress Maintenance  Industry 5.0: Adopting AI with a human-centric approach
Industry 5.0: Adopting AI with a human-centric approach  Why Trust Matters: The Role of Professional Translators in Ensuring Accurate and Engaging Translations
Why Trust Matters: The Role of Professional Translators in Ensuring Accurate and Engaging Translations  Simulating Serial Devices: Shorten Development Cycles Time and Hardware Expenditure
Simulating Serial Devices: Shorten Development Cycles Time and Hardware Expenditure  How does school management software support academic excellence?
How does school management software support academic excellence?